TMG Supplement: What It Is, Benefits, Dosage & How to Take It

Written by Tom Saleh & Reviewed by Paul Holmes.
TMG, or trimethylglycine, is a naturally occurring compound that’s been gaining major traction in longevity, health, and wellness circles.
This methyl donor is essential for supporting methylation cycles – critical biochemical processes that affect everything from gene expression to cellular energy production.
As science continues to explore its potential in enhancing energy, supporting cardiovascular health, and promoting cellular vitality, TMG is becoming a go‑to choice for those looking for effective daily support.
In this article, we’ll explore what TMG is, how it works in the body, the specific TMG benefits it offers, optimal dosage strategies, how to stack it with other wellness supplements, and most importantly, what to watch out for in terms of safety. We’ll also discuss how Naturecan’s premium TMG supplement fits into your wellness routine – offering a high‑quality way to support your own longevity. Let’s get started.
Agenda
What Is TMG (Trimethylglycine)?
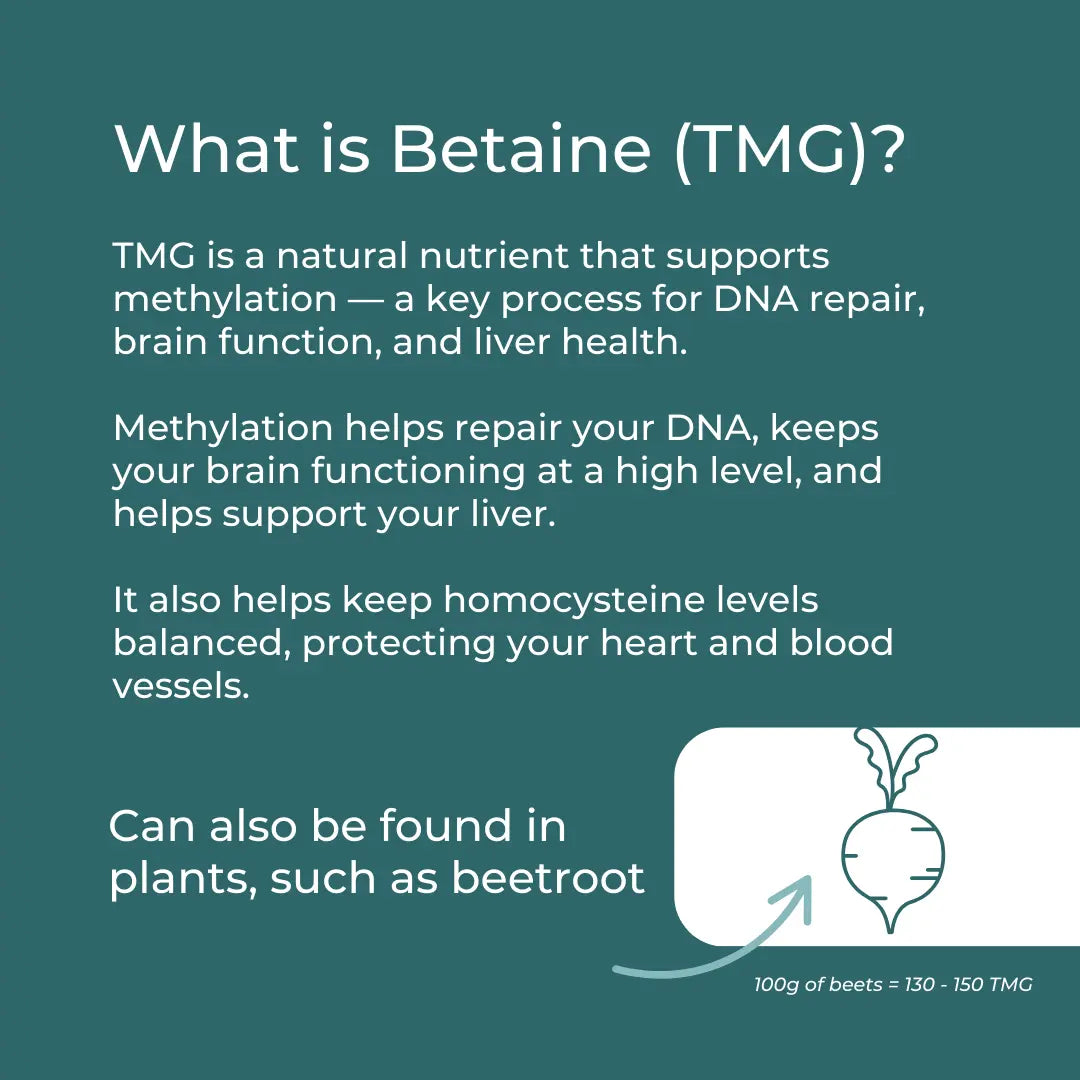
Chemically speaking, TMG is glycine that’s been decorated with three methyl groups – hence the name “trimethylglycine.”
You might also see it referred to as betaine or glycine betaine.
It’s abundant in nature, particularly in foods like sugar beets, spinach, quinoa, shellfish, and whole grains like wheat germ and bran.
Functionally, TMG serves as a methyl donor in one‑carbon metabolism.
Together with the enzyme BHMT (betaine‑homocysteine methyltransferase), it helps convert homocysteine back into methionine – a key step for healthy methylation cycles.
This pathway complements the B12/folate-dependent remethylation system and becomes especially crucial if that pathway is compromised, such as with an MTHFR gene mutation.
If you aren’t familiar with some of the terms mentioned, here’s a little insight to help you understand them better:
- Homocysteine: is a naturally occurring amino acid in the body, produced during the metabolism of methionine (another amino acid). It plays a role in methylation processes, which are critical for DNA repair, neurotransmitter production, and detoxification. However, elevated levels of homocysteine are associated with cardiovascular and neurodegenerative risks. Optimal homocysteine metabolism depends on adequate levels of B vitamins—especially B6, B12, and folate.
- Methionine: is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot produce it and it must be obtained through diet. It serves as a precursor to S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), a universal methyl donor in the body’s methylation cycle. Methionine supports detoxification, antioxidant production (via glutathione synthesis), and protein synthesis. It is particularly important for liver health, gene expression, and cellular repair.
- Methylation Cycles: The methylation cycle is a vital biochemical process where methyl groups (CH₃) are transferred between molecules to regulate gene activity, neurotransmitter function, detoxification, and cellular energy production. The cycle relies on nutrients like methionine, SAMe, folate, B12, and B6, and it helps convert homocysteine back into methionine or cysteine. Disruptions in methylation are linked to ageing, cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, and fatigue.

What The Science Says
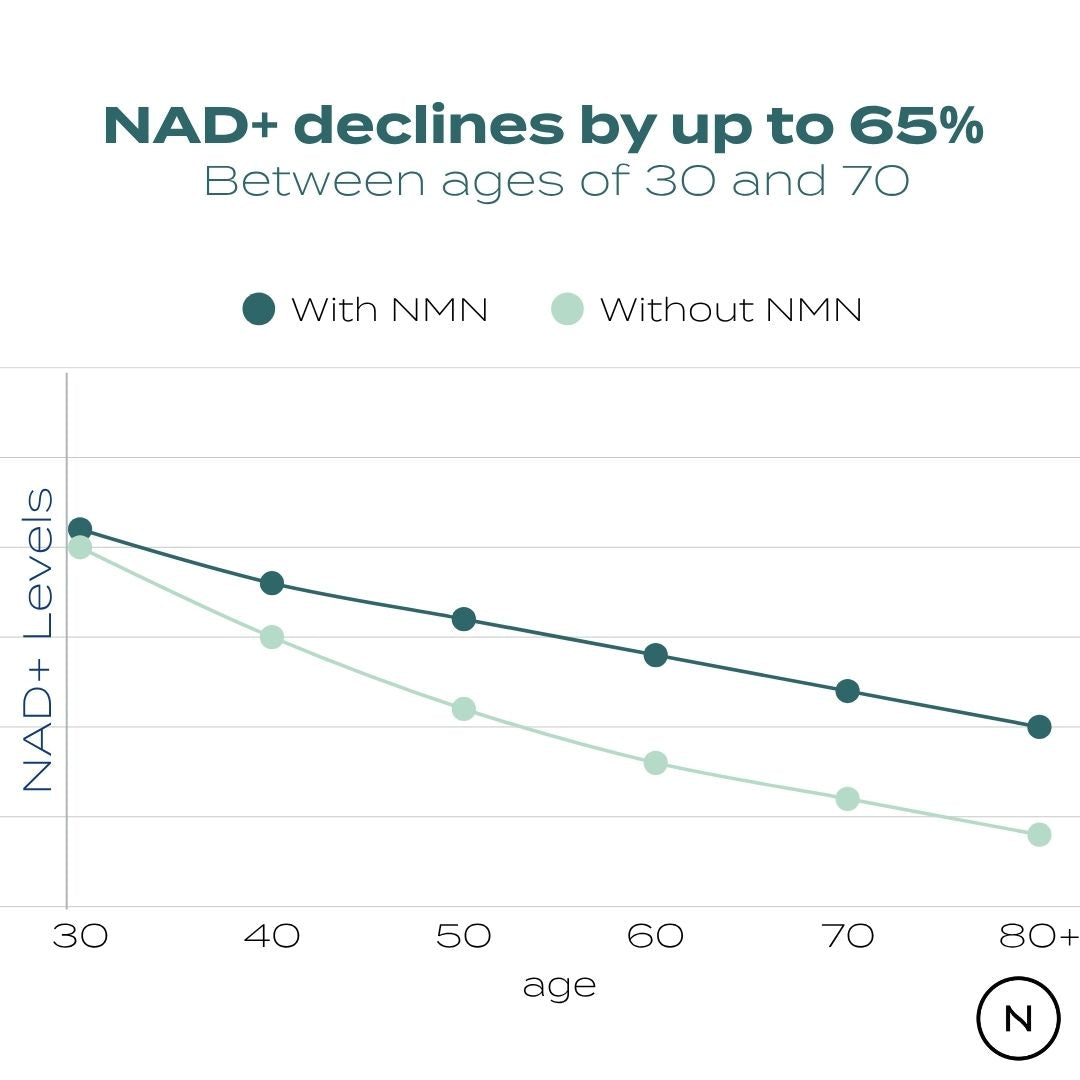
A 2025 human studies have shown that dietary doses of TMG (0.5–2 g/day) can acutely lower homocysteine – sometimes by as much as 20% – with high doses (4–6 g/day) used therapeutically to reduce homocysteine spikes after methionine intake.1
This action underpins its emerging role in longevity research, where efficient methylation and homocysteine regulation are seen as pillars of cellular health.
It’s important to note that a daily intake in excess of 4 g may significantly increase blood cholesterol levels.
6 TMG Benefits & Approved Health Claims
With many key mechanisms, there are a large number of potential TMG benefits, including:
How TMG Works in the Body
- Methylation simplified: Methylation is the addition of CH₃ groups to molecules including DNA, proteins, neurotransmitters, and lipids. TMG donates one of its methyl groups via BHMT, converting homocysteine to methionine, then dimethylglycine. Methionine then fuels SAM synthesis.
- B‑vitamin synergy: While TMG uses the BHMT route (predominant in liver/kidney), the methyl‑folate/B12 route (methionine synthase) operates in all tissues. They work together to keep methylation balanced.
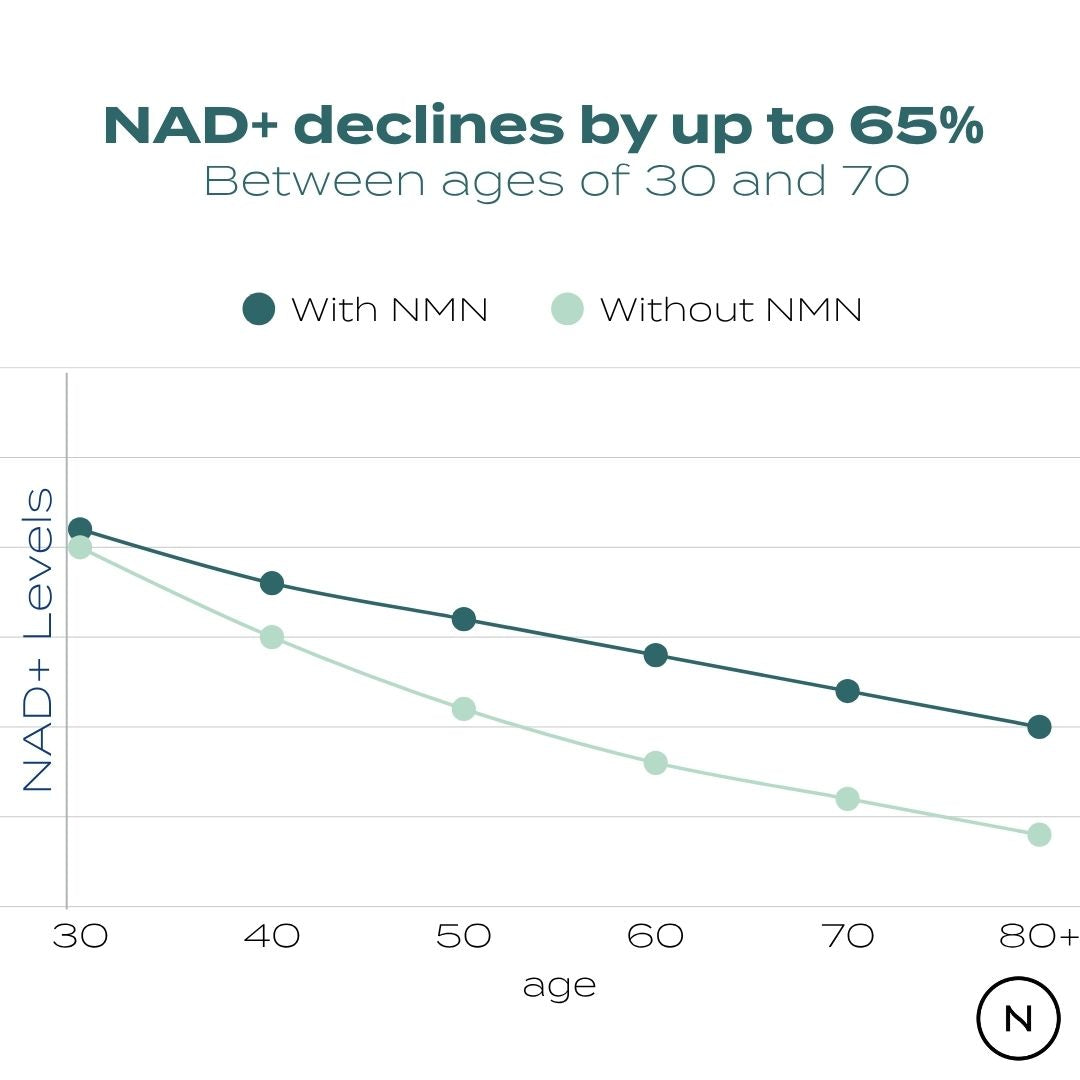
- NAD⁺ interplay: Efficient methylation helps support NAD⁺‑dependent metabolism. Using NMN with TMG may reduce methyl donor depletion caused by high NAD⁺ turnover (through NNMT enzyme) .
- Liver & detox pathways: TMG helps maintain SAM:SAH balance, enabling methylation-dependent detox enzymes and supporting glutathione production
- Cellular hydration (osmolyte action): TMG stabilises proteins and cell volume, especially under stress – like heat or dehydration.

TMG Dosage: How Much Should You Take?
The typical supplemental range for TMG and TMG benefits is 500 mg – 2,000 mg daily, with EFSA stating that someone must supplement 1.5 g/day or higher for homocysteine benefit.
4–6 g/day often used in studies reporting 10–20% homocysteine reduction.8 It’s important to note that a daily intake in excess of 4 g may significantly increase blood cholesterol levels.
Here’s some helpful guidance to help get you started:
- Start lower (500 mg–1 g/day), especially if you're new to methyl donors. Be sure to always follow serving suggestions on products and then boost your intake by consuming foods high in betaine.
- Monitor total methyl donor intake, including diet or supplements like choline, folate, SAMe.
- Decide between daily low dose vs intermittent higher cycles depending on your goals.
How to Take TMG for Best Results
- Best with breakfast or morning – supporting energy and methylation throughout the day.
- Gentle on an empty stomach, but feel free to take with food if sensitive.
- Forms include powders, capsules, or blends (Naturecan offers clean, vegan capsules).
- Stack safely with NMN, resveratrol, B‑complex, magnesium, CoQ10, and omega‑3 for enhanced longevity effects.
- Effects usually emerge over a few weeks to months.
- Do not exceed the recommended dose or mix with multiple other methyl donors without guidance.
Best Supplements to Combine with TMG
Here’s a quick, easy‑to‑read table summarising smart stacks and getting the best from your TMG benefits.
| Supplement | Synergy with TMG | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| NMN | Supports NAD⁺ + reduces methylation burden | Classic longevity pairing |
| Resveratrol | Antioxidant + SIRT support | Combine for a broader longevity network |
| Vitamin B12 | Enhances remethylation cycles | Important if low in diet or MTHFR |
| Magnesium | Cofactor in methyl metabolism | Gentle support |
| CoQ10 | Mitochondrial energy + methyl off‑load support | Helps systemic energy |
| Omega-3 | Anti‑inflammatory, cardiovascular | Complements TMG’s homocysteine action |
| Choline / Alpha‑GPC | Precursor to TMG; supports brain/liver | May reduce TMG dosage needed |
| SAMe | Methyl donor for mood & joints | Use lower dose if stacking to avoid overload |
TMG vs Other Methyl Donors
- Choline: Precursor to TMG; used primarily for brain and liver support.
- SAMe: Direct methyl donor – especially powerful for mood/joint health, but can overstimulate in some.
- Folate/B12: Works through methionine-synthase; essential for DNA synthesis and red blood cell formation.
All can be taken together to improve TMG benefits, but always monitor for overlapping effects and start with lower doses when stacking.
Improve Your Longevity Journey With Our Range
Side Effects and Safety of TMG
- Mild side effects may include stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhoea.
- High doses in some people may raise LDL cholesterol
- Rarely, large amounts may elevate methionine, especially in those with metabolic disorders
- Interactions are possible with medications affecting methylation – check with your doctor, especially if pregnant or on existing therapy.
- Long-term high-dose safety is still under study – traditional use is considered safe.
Who Should Take TMG?
- Users of NAD⁺ boosters (e.g., NMN) to reduce methylation burden.
- Those with elevated homocysteine or cardiovascular concerns..
- Anyone focused on liver health, detox, or preventing fatty liver.
- Individuals aged 40+ that are prioritising longevity and cellular maintenance.
- Athletes and physically active people for workout support and hydration.
- Individuals with MTHFR variants needing extra methyl support.
TMG Supplement by Naturecan
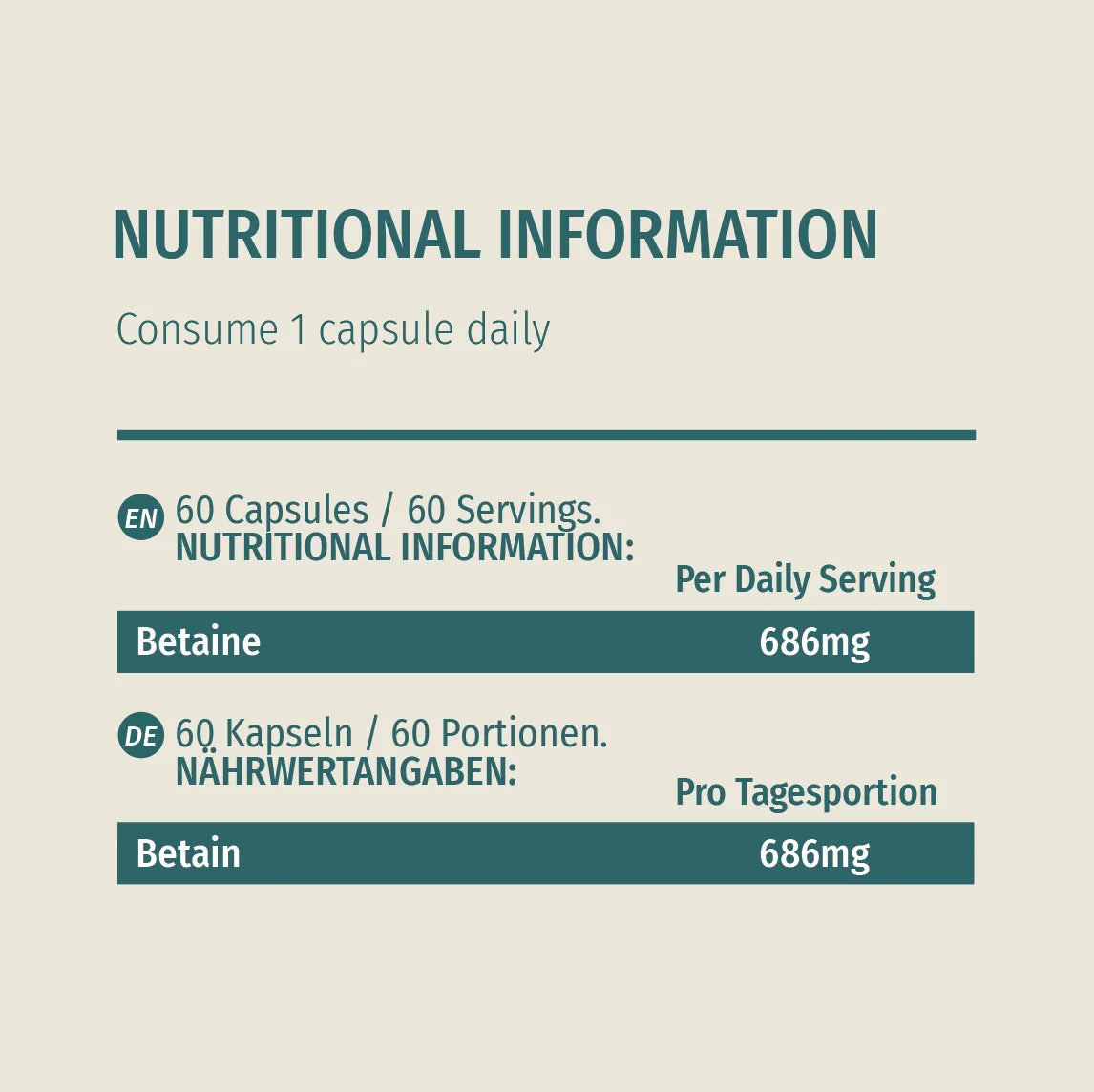
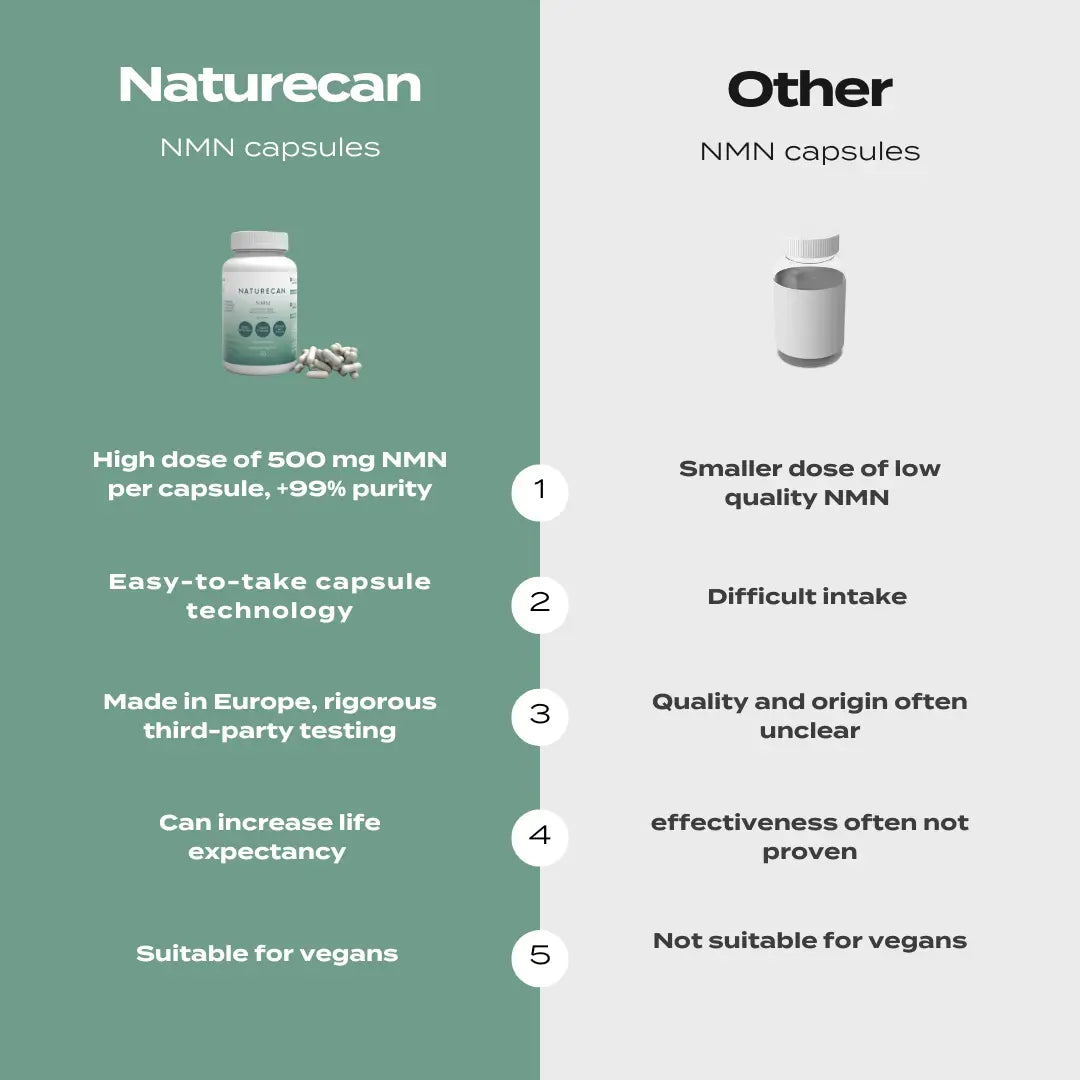
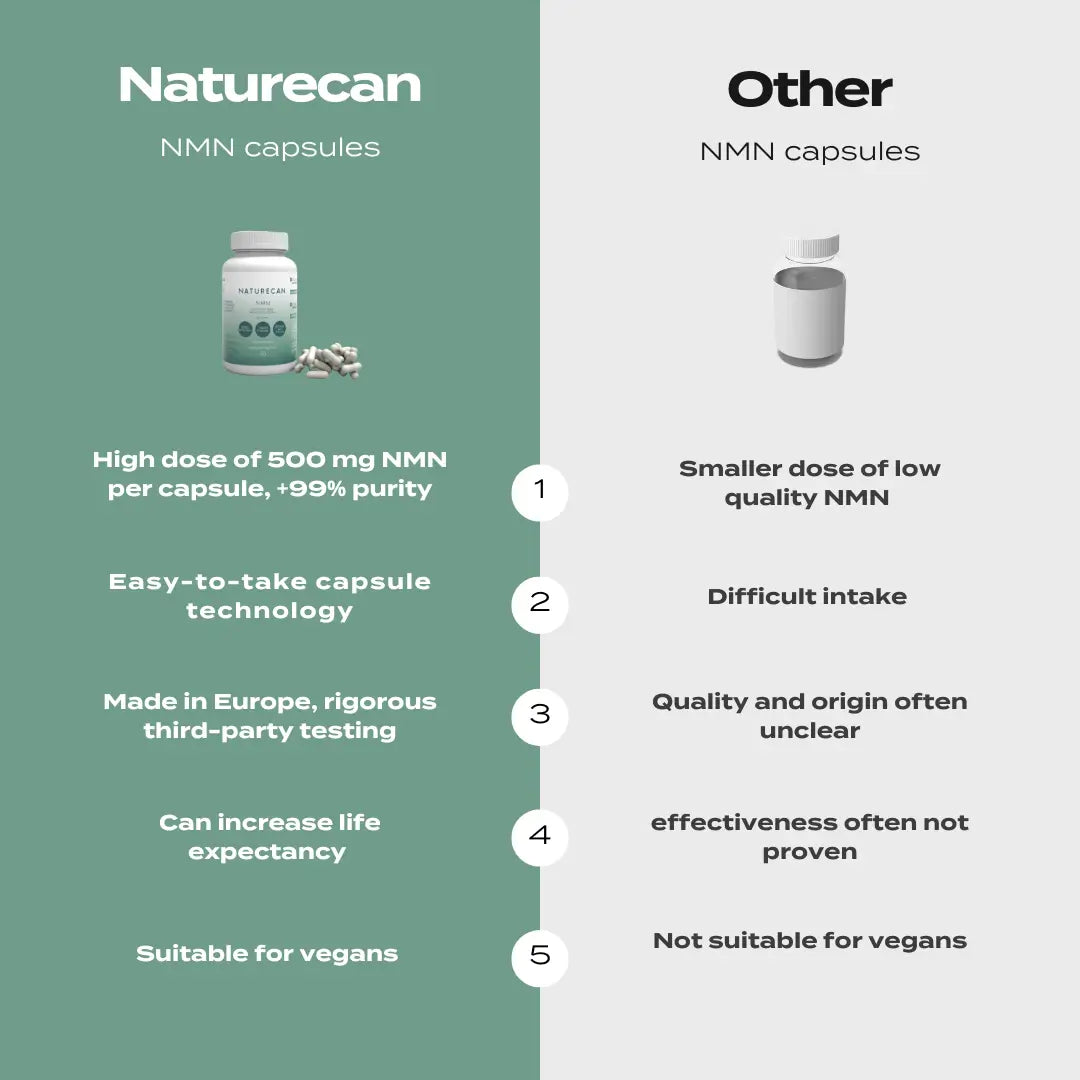
Naturecan’s TMG Trimethylglycine capsules are crafted for purity, with vegan and clean-label ingredients, and are third-party tested for quality.
With 686 mg per capsule, you can easily reach therapeutic doses or customise your intake to enhance the TMG benefits.
Each batch is lab-verified, ensuring you get a premium supplement that fits seamlessly into a science-backed longevity stack.
Final Thoughts
TMG is a versatile, natural methyl donor with significant potential to support longevity, energy, liver health, and overall cellular function.
When used thoughtfully – as part of a synergistic supplement stack or with healthy lifestyle habits – it can be a powerful addition to your wellness routine. Naturecan offers a clean, well-formulated option for those ready to explore the benefits of TMG.
If you’re curious about exploring TMG, start low, be consistent, stay aware of your biomarkers, and consider pairing it with complementary nutrients for best results.
Take a look at Naturecan’s longevity collection to build your stack and take the next step to greater, long-term wellbeing.
FAQS About TMG
What is TMG used for?
TMG is used to support methylation cycles, manage homocysteine levels, enhance liver function, improve exercise performance, and possibly promote cognitive health.
Can I take TMG with NMN and resveratrol?
Absolutely. They work synergistically: TMG supports methylation, NMN boosts NAD⁺, and resveratrol adds antioxidant and SIRT pathway support.
How long does it take for TMG to work?
You may notice subtle improvements in mood or energy within a few days. More measurable benefits – especially on homocysteine or liver biomarkers – typically show up in 4–6 weeks.
Is TMG safe to take daily?
Yes, for most people, 500 mg–2 g/day is safe long term. Higher doses (over 3 g/day) should be monitored (e.g. check cholesterol and methylation markers regularly). It’s important to note that a daily intake in excess of 4 g may significantly increase blood cholesterol levels.
What foods naturally contain TMG?
Sugar beets, spinach, quinoa, wheat germ, bran, shellfish, and some meats. Daily intake from diet generally averages 0.5–2 g/day.

Reviewed by Paul Holmes
Director of Science and Innovation at Naturecan
Testing for large pharmaceutical & tobacco companies, Paul has built a wealth of scientific and regulatory knowledge, working on regulatory submissions to bodies such as the FDA and the MHRA.
He holds a BSc in Medicinal and Biological Chemistry and sits on the UKAS CBD Food Product Approval Expert Group.